Table of contents
ToggleIn recent years, the frenzy of vehicle electrification has hit us head-on. Talaria, LiveWire, Moto Zero, and even BRP are in the race. But while all these great companies are working on electric power, some are betting more on hydrogen. The challenges of electric vehicles are limited mileage, charging time, and battery weight. More autonomy requires more energy storage capacity and therefore… more weight. And on a motorcycle, weight changes EVERYTHING! On the other hand, Kawasaki has rather focused on the hydrogen motorcycle to develop the Kawasaki H2 Hydrogen.
Kawasaki has ambitious plans to market hydrogen-powered two-wheeled vehicles in the early 2030s. This demonstrates its long-term commitment to the development of alternative fuel technologies.

How does it work?
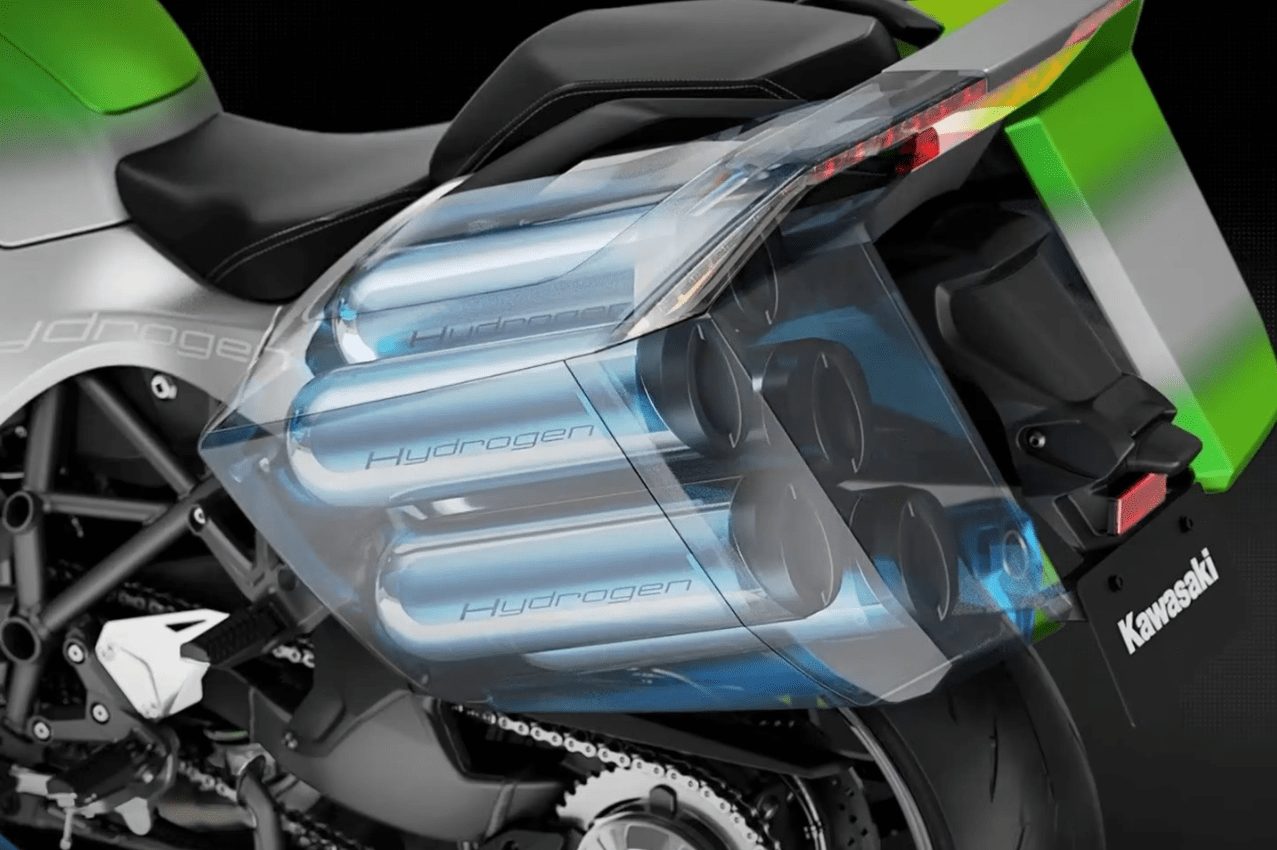
A hydrogen motorcycle engine, like that of the Kawasaki H2 Hydrogen, can operate in two ways. The first uses the principle of hydrogen combustion. The second uses a fuel cell that converts hydrogen into electricity.
Its operation is similar to that of a conventional internal combustion engine, but it uses hydrogen as fuel. Hydrogen is injected into the combustion chamber, where it mixes with oxygen (usually from the air). This mixture is then ignited, typically by a spark plug, creating an explosion. This explosion pushes the piston, generating mechanical movement.
There are two notable disadvantages. First, there is the production of NOx (nitrogen oxides) due to high combustion temperatures. Secondly, this type of engine requires twice as much air as a combustion engine to operate.
On the other hand, one of the advantages, for purists, is that unlike electric motors, once integrated into a thermal engine, the sound is still present.
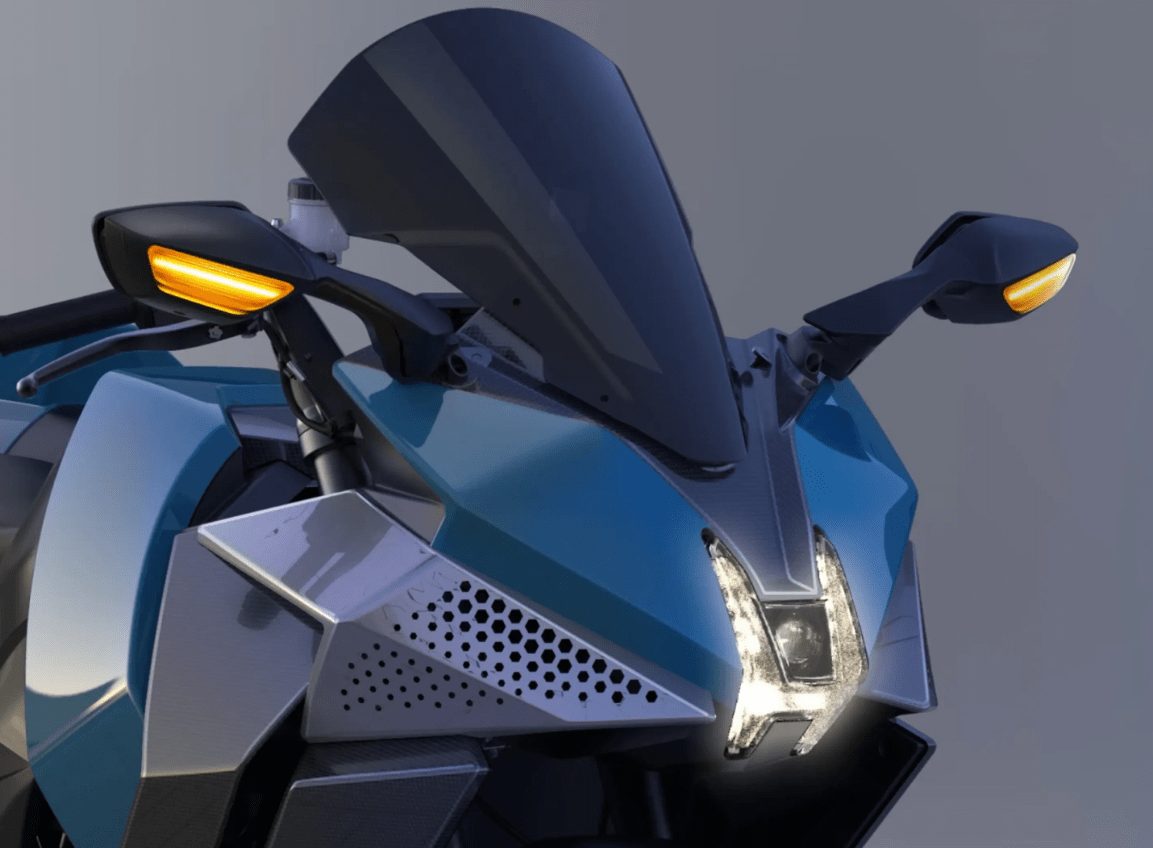

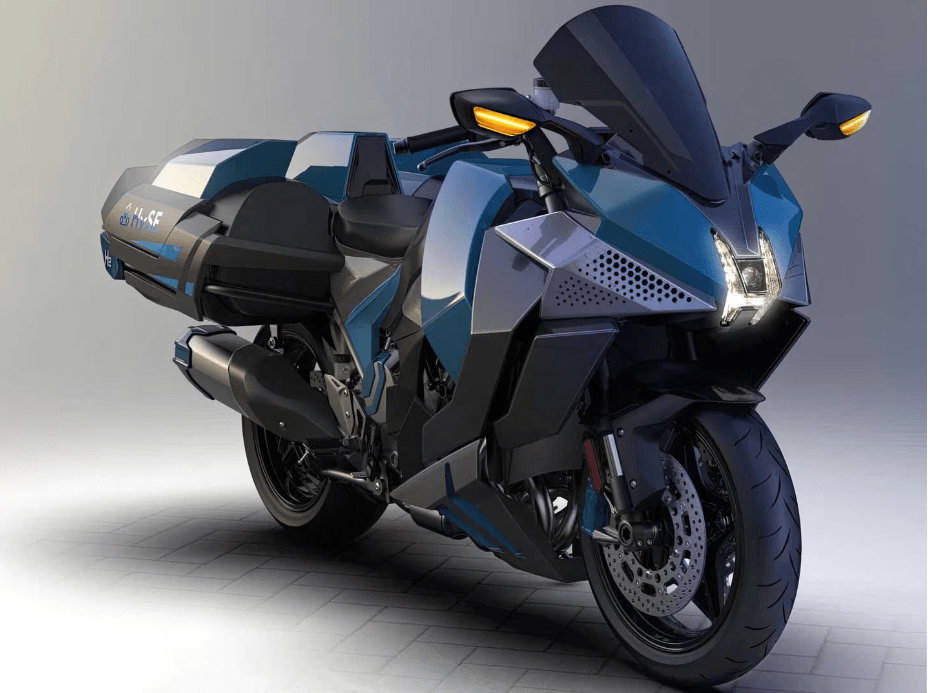
The Kawasaki H2 Hydrogen (Prototype)
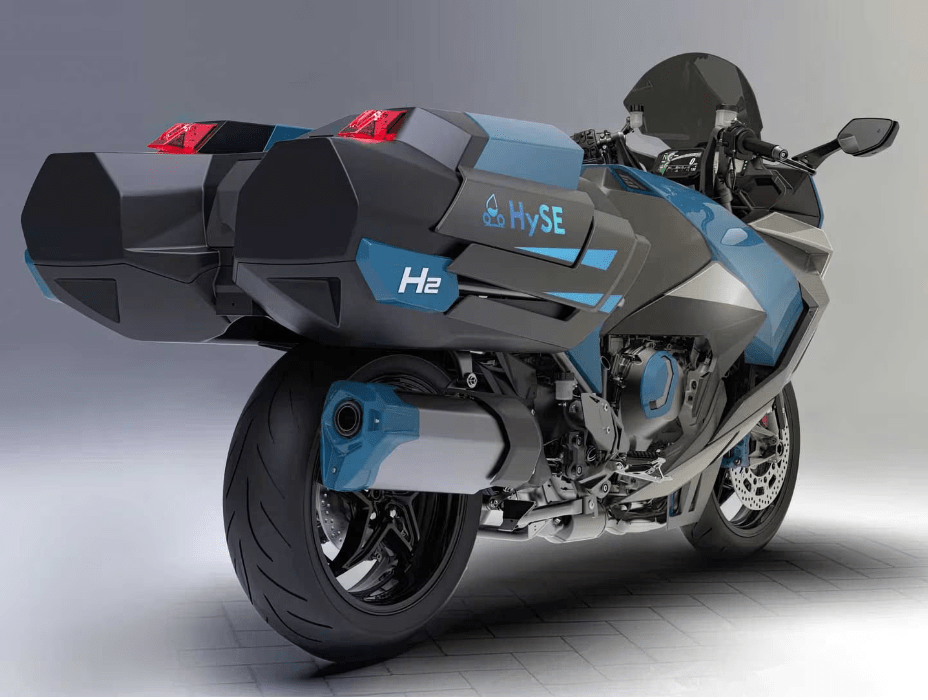
The Kawasaki H2 Hydrogen is based on the H2 SX. With this hydrogen motorcycle prototype, Kawasaki aims to create a motorcycle that refuels as quickly as a gasoline motorcycle, but with environmental consciousness. This motorcycle is also the only one to be equipped as standard with a compressor featuring a turbine spinning at 130,000 rpm to power its 1,000 cc four-cylinder engine.
Kawasaki had no choice but to adapt the look of its motorcycle to the requirements of a hydrogen engine. As can be seen in the photos, the rather massive motorcycle has a futuristic look. The side cases are actually compressed hydrogen tanks.

More Information in 2024
It is in 2024 that Kawasaki will more deeply test the capabilities of its hydrogen motorcycle prototype. That is when we will know if the Kawasaki H2 Hydrogen will truly be a pioneer in the industry. At the moment, no statistics on range, top speed, or performance have been published.
I will provide you with more details as soon as possible.
In the meantime, here are some other interesting links on the subject of hydrogen engines:
- Comment fonctionne un moteur à l’hydrogène ?
- Les risques d’un moteur à l’hydrogène.
- Est-ce qu’une voiture à l’hydrogène pollue plus qu’une voiture électrique ?